Configuration¶
Configure your project through a yml-file, which is located at .pipeline/config.yml in the master branch of your source code repository.
Your configuration inherits from the default configuration located at https://github.com/SAP/jenkins-library/blob/master/resources/default_pipeline_environment.yml.
Adding custom parameters
Please note that adding custom parameters to the configuration is at your own risk. We may introduce new parameters at any time which may clash with your custom parameters.
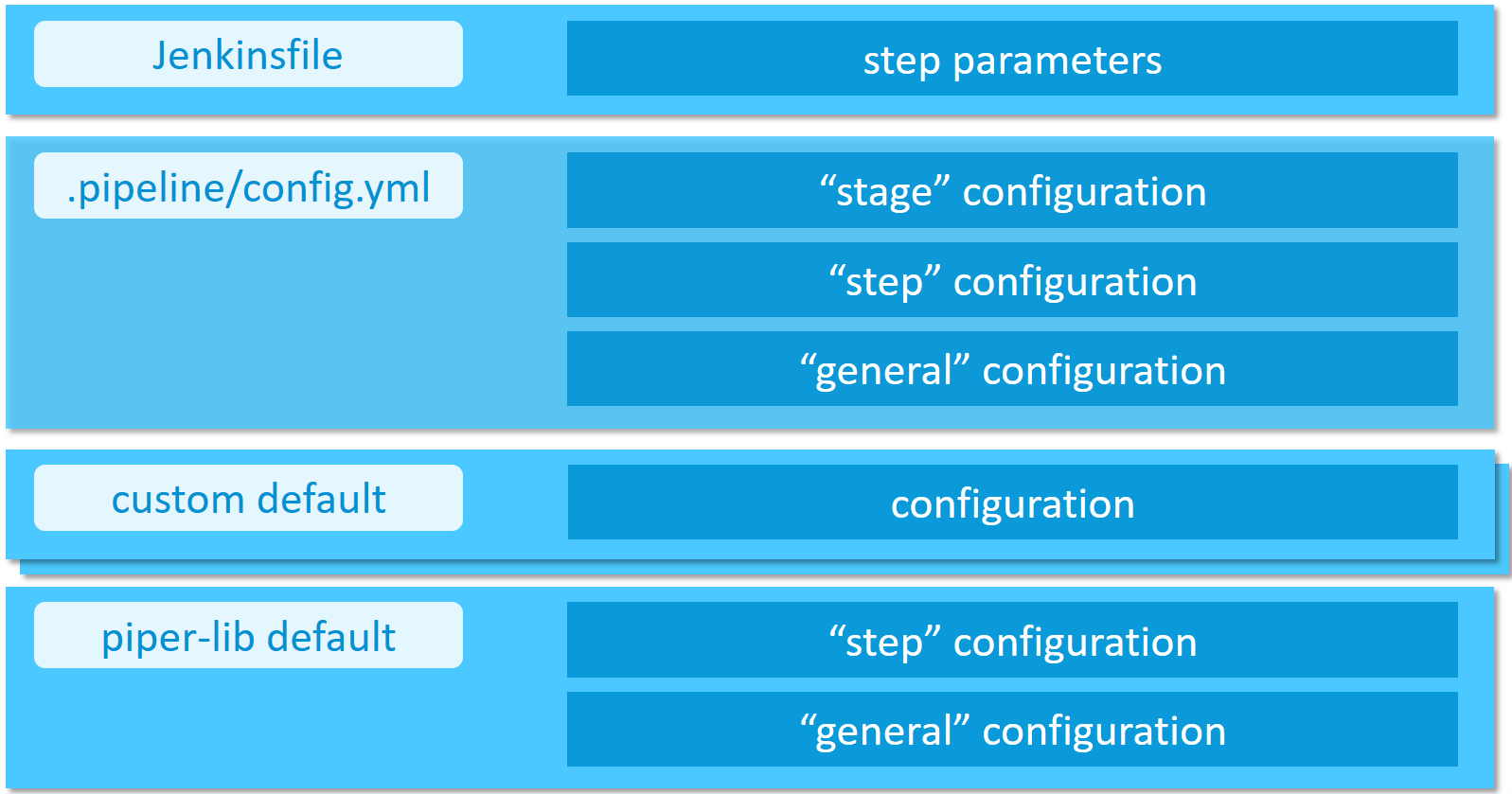
Configuration of the project "Piper" steps, as well as project "Piper" templates, can be done in a hierarchical manner.
- Directly passed step parameters will always take precedence over other configuration values and defaults
- Stage configuration parameters define a Jenkins pipeline stage-dependent set of parameters (e.g. deployment options for the
Acceptancestage) - Step configuration defines how steps behave in general (e.g. step
cloudFoundryDeploy) - General configuration parameters define parameters which are available across step boundaries
- Custom default configuration provided by the user through a reference in the
customDefaultsparameter of the project configuration - Default configuration comes with the project "Piper" library and is always available
Collecting telemetry data¶
To improve this Jenkins library, we are collecting telemetry data.
Data is sent using com.sap.piper.pushToSWA
Following data (non-personal) is collected for example:
- Hashed job url, e.g.
4944f745e03f5f79daf0001eec9276ce351d3035hash calculation is done in your Jenkins server and no original values are transmitted - Name of library step which has been executed, like e.g.
artifactSetVersion - Certain parameters of the executed steps, e.g.
buildTool=maven
We store the telemetry data for no longer than 6 months on premises of SAP SE.
Disable collection of telemetry data
If you do not want to send telemetry data you can easily deactivate this.
This is done with either of the following two ways:
-
General deactivation in your
.pipeline/config.ymlfile by setting the configuration parametergeneral -> collectTelemetryData: false(default setting can be found in the library defaults).Please note: this will only take effect in all steps if you run
setupCommonPipelineEnvironmentat the beginning of your pipeline -
Individual deactivation per step by passing the parameter
collectTelemetryData: false, like e.g.setVersion script:this, collectTelemetryData: false
Example configuration¶
general:
gitSshKeyCredentialsId: GitHub_Test_SSH
steps:
cloudFoundryDeploy:
deployTool: 'cf_native'
cloudFoundry:
org: 'testOrg'
space: 'testSpace'
credentialsId: 'MY_CF_CREDENTIALSID_IN_JENKINS'
newmanExecute:
newmanCollection: 'myNewmanCollection.file'
newmanEnvironment: 'myNewmanEnvironment'
newmanGlobals: 'myNewmanGlobals'
Sending log data to the SAP Alert Notification service for SAP BTP¶
The SAP Alert Notification service for SAP BTP allows users to define certain delivery channels, for example, e-mail or triggering of HTTP requests, to receive notifications from pipeline events. If the alert notification service service-key is properly configured in "Piper", any "Piper" step implemented in golang will send log data to the alert notification service backend for log levels higher than warnings, i.e. warnings, error, fatal and panic.
The SAP Alert Notification service event properties are defined depending on the log entry content as follows:
eventType: the type of event type (defaults to 'Piper', but can be overwritten with the event template)eventTimestamp: the time of the log entryseverityandcategory: the event severity and the event category depends on the log level:
| log level | severity | category |
|---|---|---|
| info | INFO | NOTICE |
| debug | INFO | NOTICE |
| warn | WARNING | ALERT |
| error | ERROR | EXCEPTION |
| fatal | FATAL | EXCEPTION |
| panic | FATAL | EXCEPTION |
subject: short description of the event (defaults to 'Stepsends ', but can be overwritten with the event template) body: the log messagepriority: (optional) an integer number in the range [1:1000] (not set by "Piper", but can be set with the event template)-
tags: optional key-value pairs. The following are set by "Piper": -
ans:correlationId: a unique correlation ID of the pipeline run (defaults to the URL of that pipeline run, but can be overwritten with the event template) ans:sourceEventId: also set to the "Piper" correlation ID (can also be overwritten with the event template)cicd:stepName: the "Piper" step namecicd:logLevel: the "Piper" log level-
cicd:errorCategory: the "Piper" error category, if available -
resource: the following default properties are set by "Piper": -
resourceType: resource type identifier (defaults to 'Pipeline', but can be overwritten with the event template) resourceName: unique resource name (defaults to 'Pipeline', can be overwritten with the event template)resourceInstance: (optional) resource instance identifier (not set by "Piper", can be set with the event template)tags: optional key-value pairs.
The following event properties cannot be set and are instead set by the SAP
Alert Notification service:
region, regionType, resource.globalAccount, resource.subAccount and
resource.resourceGroup
For more information and an example of the structure of an alert notification service event, see SAP Alert Notification Service Events in the SAP Help Portal.
SAP Alert Notification service configuration¶
There are two options that can be configured: the mandatory service-key and the optional event template.
Service-Key¶
The SAP Alert Notification service service-key needs to be present in the
environment, where the "Piper" binary is run. See the
Credential Management guide
in the SAP Help Portal on how to retrieve an alert notification service
service-key. The environment variable used is: PIPER_ansHookServiceKey.
If Jenkins is used to run "Piper", you can use the Jenkins credential store to store the alert notification service service-key as a "Secret Text" credential. Provide the credential ID in a custom defaults file (described below) as follows:
hooks:
ans:
serviceKeyCredentialsId: 'my_ANS_Service_Key'
!!! warning It is not possible to configure the above in the project configuration file, i.e. in .pipeline/config.yaml
Event template¶
You can also create an event template in JSON format to overwrite
or add event details to the default. To do this, provide the JSON string
directly in the environment where the "Piper" binary is run. The environment
variable used in this case is: PIPER_ansEventTemplate.
For example in unix:
export PIPER_ansEventTemplate='{"priority": 999}'
The event body, timestamp, severity and category cannot be set via the template. They are always set from the log entry.
Collecting telemetry and logging data for Splunk¶
Splunk gives the ability to analyze any kind of logging information and to visualize the retrieved information in dashboards. To do so, we support sending telemetry information as well as logging information in case of a failed step to a Splunk Http Event Collector (HEC) endpoint.
The following data will be sent to the endpoint if activated:
- Hashed pipeline URL
- Hashed Build URL
- StageName
- StepName
- ExitCode
- Duration (of each step)
- ErrorCode
- ErrorCategory
- CorrelationID (not hashed)
- CommitHash (Head commit hash of current build.)
- Branch
- GitOwner
- GitRepository
The information will be sent to the specified Splunk endpoint in the config file. By default, the Splunk mechanism is deactivated and gets only activated if you add the following to your config:
general:
gitSshKeyCredentialsId: GitHub_Test_SSH
steps:
cloudFoundryDeploy:
deployTool: 'cf_native'
cloudFoundry:
org: 'testOrg'
space: 'testSpace'
credentialsId: 'MY_CF_CREDENTIALSID_IN_JENKINS'
hooks:
splunk:
dsn: 'YOUR SPLUNK HEC ENDPOINT'
token: 'YOURTOKEN'
index: 'SPLUNK INDEX'
sendLogs: true
sendLogs is a boolean, if set to true, the Splunk hook will send the collected logs in case of a failure of the step.
If no failure occurred, no logs will be sent.
How does the sent data look alike¶
In case of a failure, we send the collected messages in the field messages and the telemetry information in telemetry. By default, piper sends the log messages in batches. The default length for the messages is 1000. As an example:
If you encounter an error in a step that created 5k log messages, piper will send five messages containing the messages and the telemetry information.
{
"messages": [
{
"time": "2021-04-28T17:59:19.9376454Z",
"message": "Project example pipeline exists...",
"data": {
"library": "",
"stepName": "checkmarxExecuteScan"
}
}
],
"telemetry": {
"PipelineUrlHash": "73ece565feca07fa34330c2430af2b9f01ba5903",
"BuildUrlHash": "ec0aada9cc310547ca2938d450f4a4c789dea886",
"StageName": "",
"StepName": "checkmarxExecuteScan",
"ExitCode": "1",
"Duration": "52118",
"ErrorCode": "1",
"ErrorCategory": "undefined",
"CorrelationID": "https://example-jaasinstance.corp/job/myApp/job/microservice1/job/master/10/",
"CommitHash": "961ed5cd98fb1e37415a91b46a5b9bdcef81b002",
"Branch": "master",
"GitOwner": "piper",
"GitRepository": "piper-splunk"
}
}
Access to the configuration from custom scripts¶
Configuration is loaded into commonPipelineEnvironment during step setupCommonPipelineEnvironment.
You can access the configuration values via commonPipelineEnvironment.configuration which will return you the complete configuration map.
Thus following access is for example possible (accessing gitSshKeyCredentialsId from general section):
commonPipelineEnvironment.configuration.general.gitSshKeyCredentialsId
Access to configuration in custom library steps¶
Within library steps the ConfigurationHelper object is used.
You can see its usage in all the Piper steps, for example newmanExecute.
Custom default configuration¶
For projects that are composed of multiple repositories (microservices), it might be desired to provide custom default configurations. To do that, create a YAML file which is accessible from your CI/CD environment and configure it in your project configuration. For example, the custom default configuration can be stored in a GitHub repository and accessed via the "raw" URL:
customDefaults: ['https://my.github.local/raw/someorg/custom-defaults/master/backend-service.yml']
general:
...
Note, the parameter customDefaults is required to be a list of strings and needs to be defined as a separate section of the project configuration.
In addition, the item order in the list implies the precedence, i.e., the last item of the customDefaults list has the highest precedence.
It is important to ensure that the HTTP response body is proper YAML, as the pipeline will attempt to parse it.
Anonymous read access to the custom-defaults repository is required.
The custom default configuration is merged with the project's .pipeline/config.yml.
Note, the project's config takes precedence, so you can override the custom default configuration in your project's local configuration.
This might be useful to provide a default value that needs to be changed only in some projects.
An overview of the configuration hierarchy is given at the beginning of this page.
If you have different types of projects, they might require different custom default configurations. For example, you might not require all projects to have a certain code check (like Whitesource, etc.) active. This can be achieved by having multiple YAML files in the custom-defaults repository. Configure the URL to the respective configuration file in the projects as described above.